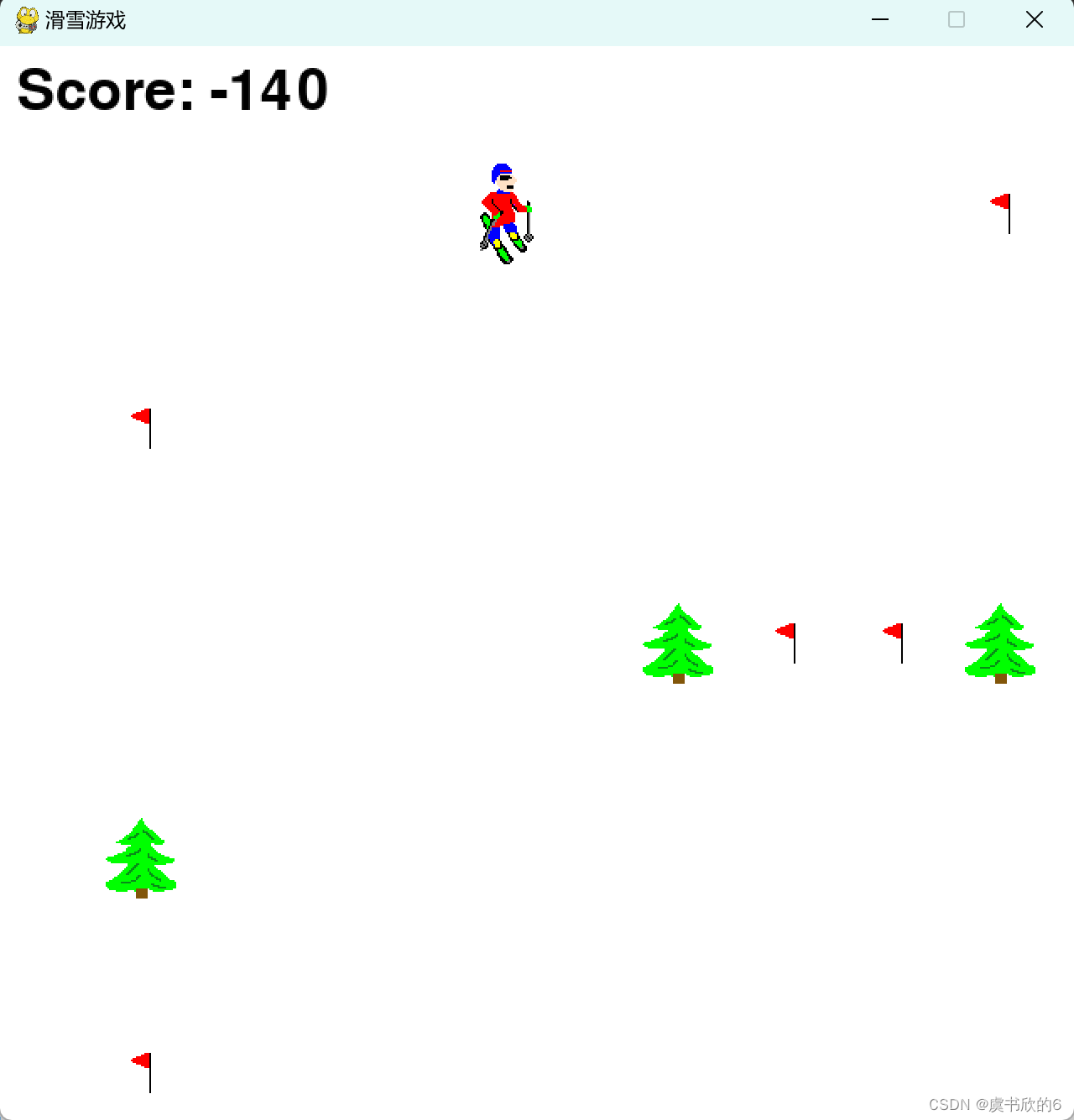
- 运行效果
- python代码
import pygame
import random
# 初始化Pygame
pygame.init()
# 设置屏幕尺寸
screen_width = 800
screen_height = 600
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((screen_width, screen_height))
pygame.display.set_caption("滑雪小游戏")
# 定义颜色
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
# 滑雪者类
class Skier(pygame.sprite.Sprite):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.image = pygame.Surface((50, 50))
self.image.fill(WHITE)
self.rect = self.image.get_rect()
self.rect.centerx = screen_width // 2
self.rect.bottom = screen_height - 10
self.speed_x = 0
def update(self):
self.speed_x = 0
keystate = pygame.key.get_pressed()
if keystate[pygame.K_LEFT]:
self.speed_x = -5
if keystate[pygame.K_RIGHT]:
self.speed_x = 5
self.rect.x += self.speed_x
if self.rect.right > screen_width:
self.rect.right = screen_width
if self.rect.left < 0:
self.rect.left = 0
# 障碍物类
class Obstacle(pygame.sprite.Sprite):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.image = pygame.Surface((50, 50))
self.image.fill(RED)
self.rect = self.image.get_rect()
self.rect.x = random.randint(0, screen_width - self.rect.width)
self.rect.y = -50
self.speed_y = random.randint(1, 5)
def update(self):
self.rect.y += self.speed_y
if self.rect.bottom > screen_height:
self.rect.x = random.randint(0, screen_width - self.rect.width)
self.rect.y = -50
self.speed_y = random.randint(1, 5)
# 创建游戏对象
skier = Skier()
obstacles = pygame.sprite.Group()
for _ in range(8): # 初始创建8个障碍物
obstacle = Obstacle()
obstacles.add(obstacle)
# 创建精灵组
all_sprites = pygame.sprite.Group()
all_sprites.add(skier)
all_sprites.add(obstacles)
# 游戏主循环
running = True
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
while running:
clock.tick(60) # 设置帧率
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
running = False
# 更新游戏对象
all_sprites.update()
# 检测碰撞
hits = pygame.sprite.spritecollide(skier, obstacles, False)
if hits:
running = False # 如果滑雪者碰到障碍物,游戏结束
# 绘制游戏
screen.fill(BLACK)
all_sprites.draw(screen)
pygame.display.flip()
# 游戏结束
pygame.quit()
- 其中涉及代码详解:
Skier 类表示滑雪者,可以通过左右箭头键来控制其移动。
Obstacle 类表示障碍物,它们从屏幕上方随机位置生成,并以不同的速度向下移动。
- 知识点总结
1. 游戏框架和库
Pygame:这是一个流行的Python库,用于创建视频游戏,包括图形和声音。它提供了显示窗口、绘制形状和图像、处理事件(如按键和鼠标点击)等功能。
Pygame Zero(可选):基于Pygame的一个更高级的库,简化了游戏开发过程,特别适合初学者。
2. 游戏循环
主循环:游戏的核心是一个不断运行的循环,称为游戏循环或主循环。它负责不断更新游戏状态、处理事件和重新绘制屏幕。
3. 图形和动画
图像加载和显示:使用Pygame加载和显示图像文件,作为游戏中的角色、背景等。
精灵(Sprite):Pygame提供了精灵类,用于管理和动画化游戏中的图像。
帧速率控制:通过控制游戏循环中的更新频率,可以调整游戏的帧速率,使其运行更加平滑。
4. 物理和碰撞检测
重力模拟:滑雪游戏中可能需要模拟重力效果,使角色向下移动。
碰撞检测:使用Pygame的矩形或圆形检测功能,判断角色是否与其他物体(如树木、岩石)碰撞。
5. 用户输入
键盘事件:监听键盘按键事件,如方向键、空格键等,用于控制游戏角色的移动和动作。
游戏菜单和暂停:通过检测特定的按键组合(如Esc键),可以实现游戏菜单的弹出和暂停功能。
6. 音效和背景音乐
音频播放:Pygame提供了音频播放功能,可以加载和播放音效和背景音乐。
音量控制:调整音效和背景音乐的音量,以适应不同的游戏场景和玩家偏好。
7. 分数和计时
计分系统:设置游戏规则,根据玩家的表现(如滑雪距离、收集的金币数量)计算分数。
计时器:使用Pygame的计时功能,记录游戏时间或特定事件的持续时间。
8. 游戏结束和重新开始
游戏结束条件:设置游戏结束的条件(如角色碰撞到障碍物、时间耗尽等)。
重新开始和退出:在游戏结束后,提供重新开始或退出游戏的选项。
9. 调试和测试
日志记录:使用Python的日志记录功能,记录游戏运行过程中的关键信息,有助于调试和测试。
单元测试:编写单元测试,验证游戏的各个模块和功能是否按预期工作。
10. 游戏优化
性能优化:通过减少不必要的绘制和计算,优化游戏的性能,使其在各种硬件上都能流畅运行。
资源管理:合理管理游戏资源(如内存、CPU时间等),避免资源泄漏和过度消耗。
转载自CSDN-专业IT技术社区
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/cxh666888_/article/details/143455938